What is Edge Computing?
At its core, edge computing represents a departure from the traditional centralized model of data processing. In contrast to the dependence on a centralized cloud-based system, this approach underscores localized computation and storage near the data source. The primary goals are to reduce latency, optimize bandwidth, and enhance security and privacy.
Key Characteristics of Edge Computing
● Proximity:
The hallmark of edge computing is its proximity to the data source, minimizing the physical distance data must traverse. This localization ensures a swift and efficient processing cycle.
● Low Latency:
Immediate processing at the edge translates to low latency, a critical factor for applications demanding real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
● Decentralized Architecture:
Unlike the centralized model, edge computing adopts a decentralized architecture. This means computing capabilities are distributed across various nodes rather than relying on a singular processing hub.
Benefits of Edge Computing
● Reduced Latency:
Edge computing’s ability to process data at the source minimizes the delay between data generation and processing. This is indispensable for applications requiring immediate responses, like autonomous vehicles navigating complex environments.
● Bandwidth Optimization:
By processing data locally, edge computing eases the strain on network bandwidth. This optimization proves especially valuable for applications dealing with substantial data volumes, ensuring efficient data flow.
● Enhanced Security and Privacy:
Localizing data processing enhances security by keeping sensitive information close to its source. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and provides a robust foundation for safeguarding critical information.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
● Smart Manufacturing:
Edge computing facilitates real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime in industrial settings.
● Smart Grids:
In the energy sector, edge computing plays a pivotal role in optimizing grid management, allowing for rapid responses to fluctuations in demand and ensuring a stable energy supply.
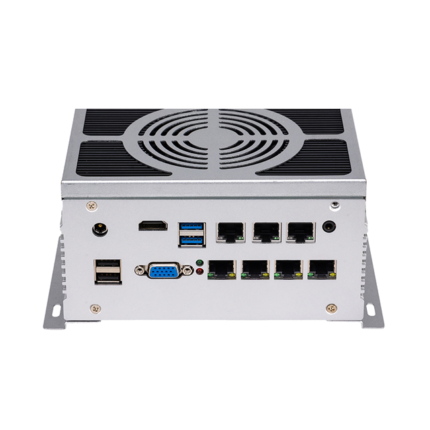
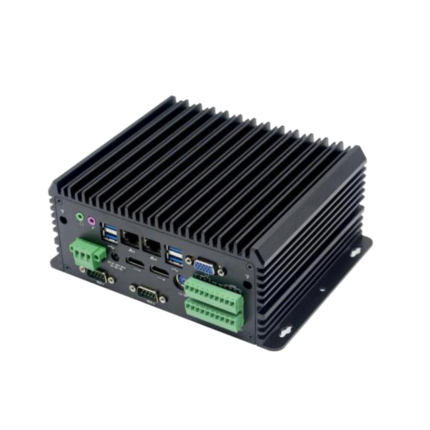
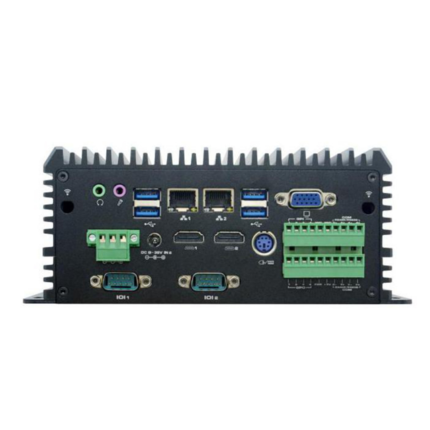
| Model | NANO-100 | |||
| Processor | Intel® Celeron® J1900/ N2840 Processor |
Intel®Core™ 4th/5th Gen 13/15/17 Processor |
Intel® Celeron® J4125 Processor |
|
| Memory | DDR3L 4G/8G | DDR4L 4G/8G/16G |
||
| Storage | 1*MSATA, 1*SATA | |||
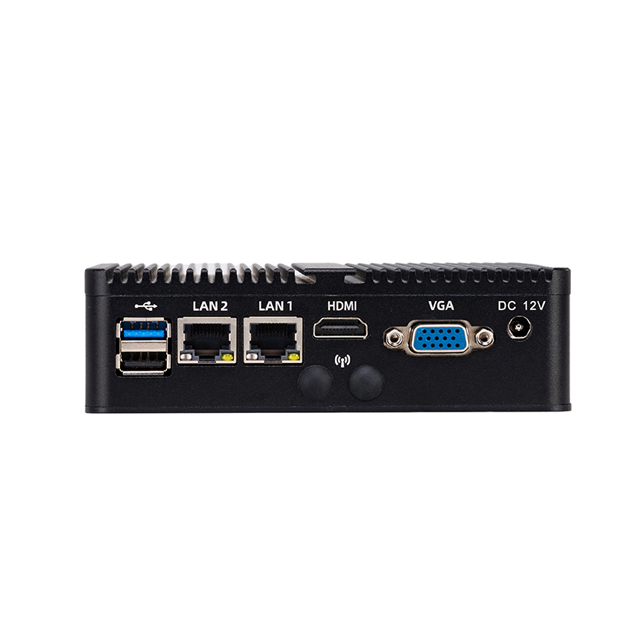
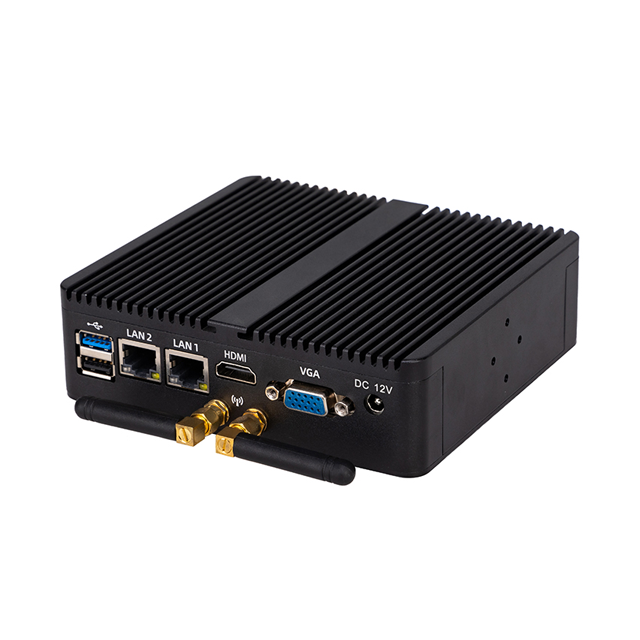
| Net work | 2 *Realtek RTL8111Gigabit-NIC | |||
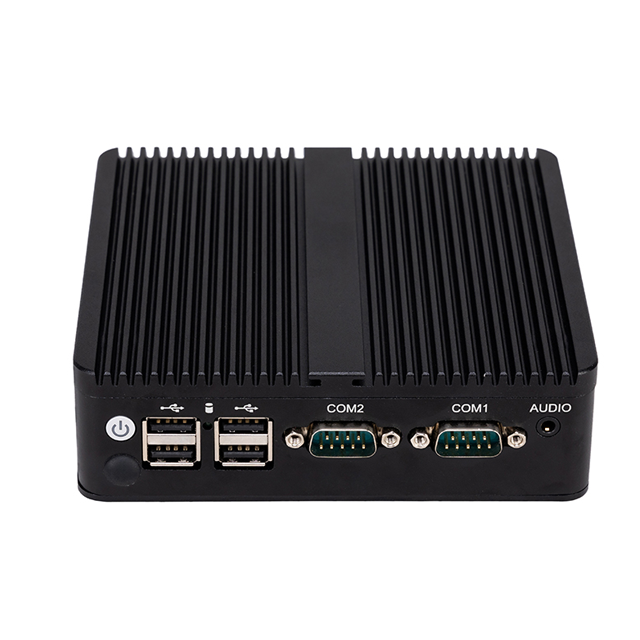
| COM | 2 *COM( COM1-2 support RS485) | |||
| USB | 6 *USB | |||
| Display | 1*HDMI, 1*VGA | |||
| Other interfaces | 1* input x4 / output x4 GPIO | |||
| Expand slot | 1*MINI-PCIE(support WIFI/4G module) | |||
| Operating system | Windows/Linux | |||
| Power Input | DC12V | |||
| Size included rack (mm) | 178.4x127x60 | 136x127x40 | 178.4x127x60 | |
| Weight (kg) | 1.00 | |||
| Mounting Options | Wall-mounted / Desktop | |||
| Operating Temperature | -20 ~ +60°C | |||
| Storage Temperature | -20 ~ +70°C | |||
| Storage Humidity | 5 ~ 95% | |||
| Packaging Information | 1 *Master, 1 *Adapter, 1* Power Supply Cable | |||